반응형
반응형
💡 Java에서 Thread 생성 및 실행 정리
🔄 1️⃣ Thread 생성
- Java에서 모든 스레드 관련 속성과 메서드는 Thread 클래스에 정의되어 있습니다.
- Thread를 생성할 때는 Thread 클래스 객체를 생성합니다.
- 생성자에 Runnable 인터페이스를 전달해야 합니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Code that will run in a new thread.
}
});
}
}
🚀 2️⃣ Thread 실행
- 생성된 Thread 객체는 start() 메서드를 호출해야 실행됩니다.
- thread.start(); → JVM이 새로운 스레드를 생성하여 운영체제에 전달합니다.
thread.start();
👁️ 3️⃣ 실행 중인 스레드 확인
- Thread.currentThread().getName()으로 현재 실행 중인 스레드 이름을 확인할 수 있습니다.
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "before starting ");
thread.start();
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "after starting ");
📝 4️⃣ 최종 코드 및 실행 결과
package thread.create1;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Code that will run in a new thread.
// 1
System.out.println("We are now in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
//2
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "before starting ");
thread.start();
// 3
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "after starting ");
}
}
실행 결과 :
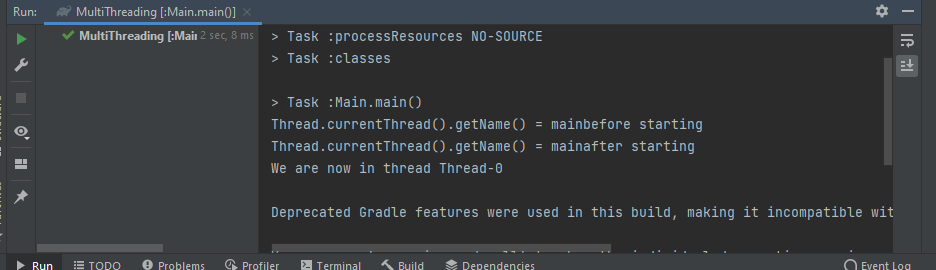
실행 순서:
- 메인 스레드에서 "before starting" 출력
- thread.start(); → JVM이 새로운 스레드 생성
- 메인 스레드에서 "after starting" 출력
- 새롭게 생성된 쓰레드에서 "We are now in thread..." 출력
💡 이유:
- thread.start();는 비동기적으로 실행되기 때문에, 메인 스레드는 계속 진행하며 2번과 3번이 먼저 출력됩니다.
- 이후에 새로운 스레드가 실행되면서 4번이 출력됩니다.
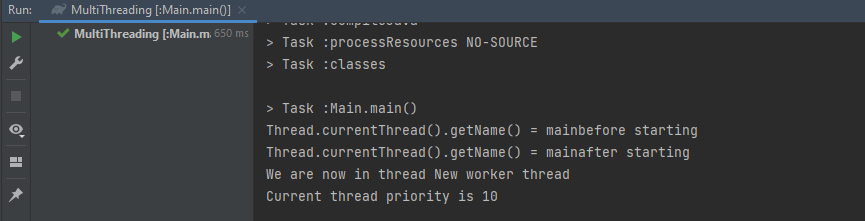
⚙️ 5️⃣ Thread 우선순위 설정
- 스레드의 이름과 우선순위를 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 우선순위 설정 → thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Code that will run in a new thread.
// 1
System.out.println("We are now in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("Current thread priority is " + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
});
thread.setName("New worker thread");
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
- MAX_PRIORITY: 10
- MIN_PRIORITY: 1
- NORM_PRIORITY: 5
우선순위 설정은 복잡한 멀티스레드 환경에서 실행 순서와 속도에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
위 코드를 실행해도 동일한 순서가 나온다.
아직까지는 수행차이가 없지만 추후 복잡한 멀티쓰레드 환경에 코드를 실행하고 우선순위등 결정해야할때 아주 중요한 역할을 한다.
실행 결과 :
💡 Thread 생성 방법 2: Thread 클래스 상속
🔄 1️⃣ Thread 클래스 상속하기
- 기존에 사용한 Runnable 인터페이스 구현 대신, Thread 클래스를 상속하여 직접 스레드를 생성할 수 있습니다.
- Thread 클래스는 이미 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하고 있기 때문에, run() 메서드만 오버라이드하면 됩니다.
✍️ 2️⃣ 코드 예시
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new NewThread();
thread.start();
}
public static class NewThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName() = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}
🚀 4️⃣ 특징 및 장점
특징설명
| ✔️ 코드가 간결해짐 | Runnable을 따로 구현할 필요 없이 run()만 오버라이드하면 됨 |
| ✔️ 명확한 클래스 정의 | Thread 클래스를 상속받기 때문에 명확한 역할을 가진 클래스 생성 |
| ✔️ 추가 메서드 사용 가능 | Thread 클래스의 다양한 메서드 (getName(), getId(), sleep())를 바로 사용 가능 |
❌ 5️⃣ 단점
- Java는 단일 상속만 허용하므로, 다른 클래스를 상속받고 싶다면 사용할 수 없습니다.
- 이 경우 Runnable 인터페이스 구현 방식이 더 유연합니다.
🔍 6️⃣ 결론
- Thread 상속 방식: 코드가 간단하고 명확하지만, 단일 상속 제약이 있음
- Runnable 구현 방식: 다중 상속이 필요할 때 더 유리함
반응형
'강의 자료 > 고성능을 강조한 Java 멀티스레딩, 병행성 및 병렬 실행 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 섹션 3 : 스레딩 기초 (스레드 연결) (1) | 2025.05.18 |
|---|---|
| 섹션 3: 스레딩 기초 - 스레드 조정 (0) | 2025.05.18 |
| 멀티스레드를 활용한 금고 해킹 시뮬레이션 (자바 구현) (2) | 2025.05.18 |
| 색션 1 : 개요 (프로세스, 쓰레드, 멀티프로세스 vs 멀티쓰레드) (0) | 2025.05.17 |


