반응형
요새 계속 코테만 보는 것 같은 느낌적인 느낌..
1. 피포나치 재귀 호출로 구해보기
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
public class Fibonacci {
public static int fibo(int number) {
if(number == 0) return 0;
if(number == 1) return 1;
return fibo(number - 1) + fibo(number - 2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(fibo(number));
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
2. 스트링 순서 바꾸기 version 1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
public class PartialWordReverse {
public static void printWords(String str) {
int i = 0;
for(; i < str.length() && str.charAt(i) != ' '; i++) {
System.out.print(str.charAt(i));
}
String words = "";
for(; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) != ' ') {
words += str.charAt(i);
} else {
System.out.print(new StringBuilder(words).reverse().toString() + " ");
words = "";
}
}
System.out.print(words);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString());
System.out.println("=============");
printWords(str);
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|

version1 에서는 앞 단어와 그리고 맨 뒤 단어는 정상적으로 출력이되고 중간 단어들은 순서를 바꿔서 출력하기
version2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
public class PartialWordReverseVowl {
public static boolean isVowel(char c) {
return (c == 'a' || c == 'A' || c == 'e'
|| c == 'E' || c == 'i' || c == 'I'
|| c == 'o' || c == 'O' || c == 'u'
|| c == 'U');
}
public static String partialWorrdReverse(String str) {
int i = 0;
int j = str.length() - 1;
char[] str1 = str.toCharArray();
while (i < j) {
if (!isVowel(str1[i])){
i++;
continue;
}
if (!isVowel(str1[j])){
j--;
continue;
}
char temp = str1[i];
str1[i]= str1[j];
str1[j]= temp;
i++;
j--;
}
;
return String.valueOf(str1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println(partialWorrdReverse(str));
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|

버젼2에서는 모음만 비교해서 바꿔주기
3. Stack를 사용해서 Queue방식 출력
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
import java.util.Stack;
public class QueueSolution {
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
int front = 0;
// Push element x to the back of queue.
public void push(int x) {
if (s1.empty())
front = x;
}
public void pop() {
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty())
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
public int peek() {
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
return s2.peek();
}
return front;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueSolution solution = new QueueSolution();
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|

stack은 lifo 방식이기때문에 push했을때 원래는 5 4 3 2 1순서되로 출력이되야하지만
push, pull, peek, empty의 조건들을 바꿔서 1이먼저 출력!
4. Implementing queue using stack
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class QueueUsingStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueStack qs = new QueueStack();
qs.stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
qs.stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
qs.enQueue(qs, 1);
qs.enQueue(qs, 2);
qs.enQueue(qs, 3);
System.out.println(qs.deQueue(qs));
System.out.println(qs.deQueue(qs));
System.out.println(qs.deQueue(qs));
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println("using queue example");
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
q.add(i);
}
for(Integer e : q) {
System.out.println(e);
}
q.remove();
System.out.println(q.peek());
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
import java.util.Stack;
public class QueueStack {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public void push(Stack<Integer> qs, int n) {
}
public int pop(Stack<Integer> qs) {
if(qs.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Nothing is in");
System.exit(0);
}
return x;
}
public void enQueue(QueueStack qs, int n) {
push(qs.stack1, n);
}
public int deQueue(QueueStack qs) {
int x = 0;
if(qs.stack1.isEmpty() && qs.stack2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("queue is empty");
System.exit(0);
}
if(qs.stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!qs.stack1.isEmpty()) {
x = pop(qs.stack1);
push(qs.stack2, x);
}
}
x = pop(qs.stack2);
return x;
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
queue의 enqueue 랑 dequeue사용
솔직히 이해는 조금 부족함
5. Two Sum Method
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
public class TwoSumMethods {
public static int[] bruteForce(int[] numbers, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numbers.length; j++) {
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) {
return new int[] { i, j };
}
}
}
return new int[] {};
}
public static int[] sortedMethod(int[] numbers, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = numbers.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
System.out.println(numbers[left] + numbers[right]);
if(numbers[left] + numbers[right] == target) {
return new int[] {left, right};
} else if(numbers[left] + numbers[right] < target) {
left++;
System.out.println("left +");
} else {
right--;
System.out.println("right -");
}
}
return new int[] {};
}
public static int[] hashMethod(int[] numbers, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> numMap = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
int complement = target - numbers[i];
if(numMap.containsKey(complement)) {
} else {
}
}
return new int[] {};
}
// public static Vector<Integer> twoSum(Vector<Integer> nums, int target) {
// Vector<Integer> vec = new Vector<Integer>(100);
// for(Integer e : nums) {
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// int complement = target - nums.get(i);
// if(vec.contains(complement)) {
// Vector<Integer> vecs = new Vector<Integer>();
// return vecs;
// } else {
// }
// }
// return new Vector<Integer>();
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int[] numbers = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
numbers[i] = scan.nextInt();
}
// Vector<Integer> numbers = new Vector<Integer>();
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// }
int target = scan.nextInt();
// twoSum(numbers, target);
// System.out.println("asdfasdfsd");
// for(Integer e : twoSum(numbers, target)) {
// }
//
int[] result = hashMethod(numbers, target);
if (result.length == 2) {
System.out.println(result[0] + " " + result[1]);
} else {
System.out.println("found no results");
}
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|

6. Happy Number
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package algo.codingtests.kongstudios;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class HappyNumber {
public static int checkSquare(int n) {
int squareNum = 0;
while(n != 0) {
squareNum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
return squareNum;
}
public static boolean isHappyNumber(int n) {
Set<Integer> st = new HashSet<Integer>();
System.out.println("number before is " + n);
while(st.add(n)) {
// n = checkSquare(n);
int squareNum = 0;
while(n != 0) {
squareNum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
n = squareNum;
System.out.println("after check is " + n);
}
return (n == 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(isHappyNumber(n) ? "happy":"not happy");
}
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#e5e5e5text-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
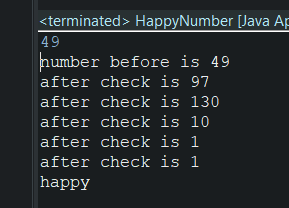
코테 하면서 오늘 새로운것들 많이 배웠다
stack queue사용법, happy number algo, two sum algo 그리고 string reverse조건으로 결정하기
반응형
'IT > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 5단계(2577) (0) | 2019.11.28 |
|---|---|
| 백준 5단계(2920) (0) | 2019.11.28 |
| 기초 알고리즘(38번 치킨쿠폰 재귀) (0) | 2019.11.24 |
| 백준 5단계(2562) (0) | 2019.11.24 |
| 백준 5단계(10818) (0) | 2019.11.23 |