Java.lang.OutOfMemoryError ==not able to use heap because heap is full, NEED TO CHECK FOR MEMORY LEAKS!!!
Garbage collection has 3 steps:
Mark- starts from root node of your application, walks object graph and marks objects that are reachable as live
Sweep/delete – delete unreachable objects, sweeps from heap
Compacting- Arranging everything in order, when unreachable objects are sweeped, there are holes empty places so then compacting comes in and arranges objects in order.
Heap is divided into two spaces, young generation and old(tenured) generation :
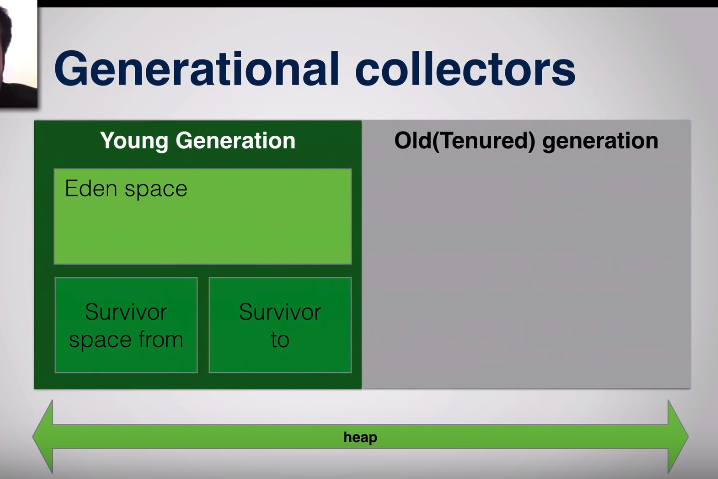
Eden space – a place where new objects are created, references to a book of genesis
When eden space is full, that is when minor(small) garbage collector kicks in removes unreachable objects and moves them to survivor space
Survivor space - Having two survivor space prevents compacting step to be used again.
Old generation – a place in heap where long survived objects are stored
Major garabage collector kicks when old generation is almost full, marks, sweep and compacts new and old generation. Application comes to a halt while this is happening.
-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold = how many times object need to survive to be placed into old generation
*Performance*
responsiveness/latency- how quickly an application response with a requested piece of data
ex. If a ui on a web application focuses on responsiveness, large pause times are not acceptable.
Throughput = throughput focuses on maximizing the amount of work by an application in a specific period of time.
Ex. The number of jobs that a batch of program can complete in an hour
The number of database queries that can be completed in an hour
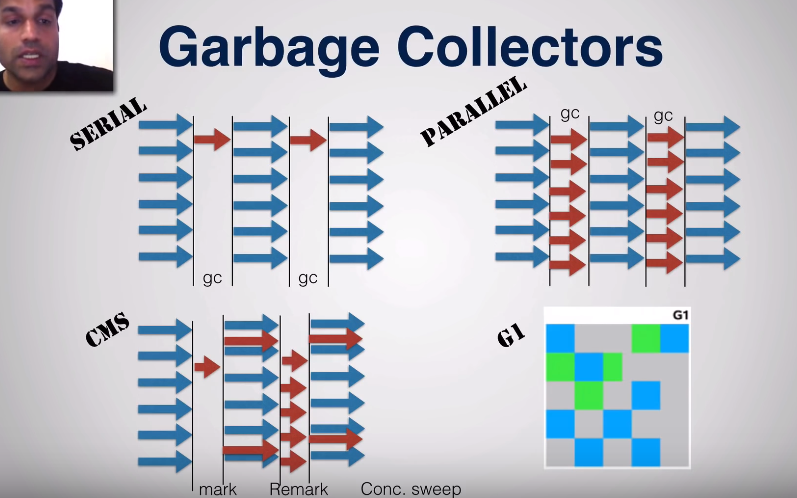
*Type of garbage collectors*
A serial garbage collector – basic garbage collector that runs in a single thread, can be used for basic applications
Pause, runs, pause, runs
A concurrent collector – a thread that performs gc along with application execution as the application runs, does not wait for the old generation to be full – stop the world only during mark/re-mark
A parallel collector - Uses multiple cpus to perform gc. Multiple threads doing mark/sweep etc. does not kick in until heap is full or near full.
Use concurrent collector when(responsiveness/latency)
There is more memory
There is high number of cpus to spare
Application demands short pauses
Use a parallel collector when(throughput!)
Application demands high throughput and can withstand pauses
Most application use concurrent garbage collector because of high responsiveness! Of course!
As of Java 1.7, g1 was introduced
G1 divides heap into small regions. When a certain region has a lot of unreachable objects, gc kicks in. g1 does not care for young or old or eden survivor space.
- Parallelism and concurrency together
- Low pauses with fragmentation
- Better heap utilization
Uptil 1.6, parallelgc was default
1.7 + g1gc is the default
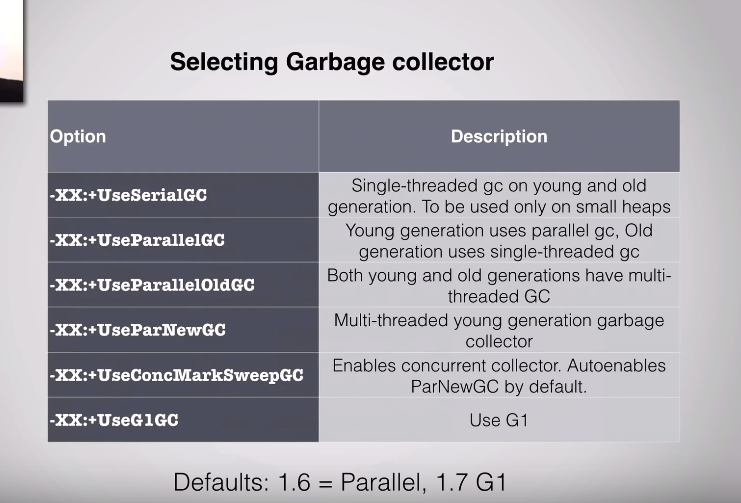

Xmsvalue = setting the minimum value to heap
Xmxvalue = maxium value to heap(default 256)
Xx:newratio=ratio (2means 1/3 Y + 2/3 O(T))
Xx:newsize=size how much amount of memory set aside for eden space
Xx:permsize a size assigned to meta-data(static class data etc)
Xx:maxpermsize def 64m
게임회사에서 면접을 보면서 대답을 못 한 질문이 많았지만 개발자로서 꼭 알아야 하는 이론인데 공부를 하지 않아서 답변 못 했던 질문이 2개였는데 하나가
1. 가비지 컬렉터가 어떻게 돌아가는지
2. Big O에 대해서
전에 자바 메모리 구조 포스트에 올렸듯이 meta-data에는 static 그리고 클래스 자료들이 저장되고, stack 안에서는 local variable들이 저장되면서 객체의 변수도 같이 저장되는데 heap 영역에서 객체의 자료가 저장된다. stack에서는 heap의 참고 주소만 가지고 있어서 만약 heap에서 자료를 참고하지 않으면 가비지 컬렌터가 돌아간다는 까지 알고 있었는데, 힙 영역 안에서 어떻게 작동하는 원리를 물어보셔서 많이 당황한 기억이 난다.
그래서 집에 와서 공부한 게 빅오랑 가비지 컬렉터다.
영어로 배워서 영어로 위에 설명을 적었는데 나중에 면접 가서 설명은 한국말로 해야 해서 간략하게 정리해보겠습니다
가비지 컬렉터는 3가지 단계로 작동을 한다
mark, sweep, compact
힙안에는 new generation 그리고 old generation이 존재한다
new generation 안에는 eden 그리고 2개의 survivor 영역
old generation은 그냥 old generation
가비지 컬렉터는 new generation에 eden이 다 찾을 때 minor garbage collector가 작동하면서 참조 안 되는 객체는 지우면서 참조되는 자료는 survivor 영역으로
만약 오래 존재하는 자료면 old generation으로 이동
old generation 메모리 영역이 거의 다 찼을 때 major gc 발동. major gc는 new와 old다 mark sweep compact 함
이런 식으로 메모리가 정리된다
가비지 컬렉터의 종류는 현재 4가지
원래는 parallel gc 를 default로 사용했지만 1.7 이후부터 g1 gc 사용
g1서부터는 old new generation 구분 없이 영역을 나누어서 해당 영역이 차면 gc 발동, g1이 parallel 그리고 concurrent와 같이 사용하는 느낌
다음 면접 때 물어보면 확실히 설명할 수 있을 것 같다
'IT > ETC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이것이 자바다 노트2(스레드 + 멀티스레드) (0) | 2019.12.14 |
|---|---|
| 이것이 자바다 노트1 (0) | 2019.12.09 |
| Comparable vs Comparator (0) | 2019.12.01 |
| Algorithm time complexity (2) | 2019.12.01 |
| 자바 메모리 구조 (0) | 2019.11.23 |

